iOS虚拟定位几种方法:
- 使用Xcode自带
Simulate Location,通过GPX文件修改; - 通过Mac/PC应用修改手机定位;
- 通过外设修改手机定位;
- 逆向App,hook定位经纬度;
Xcode Simulate Location使用
要使用 Xcode 的Simulate Location,可以按照以下步骤:
- 打开 Xcode 并新建一个iOS项目;
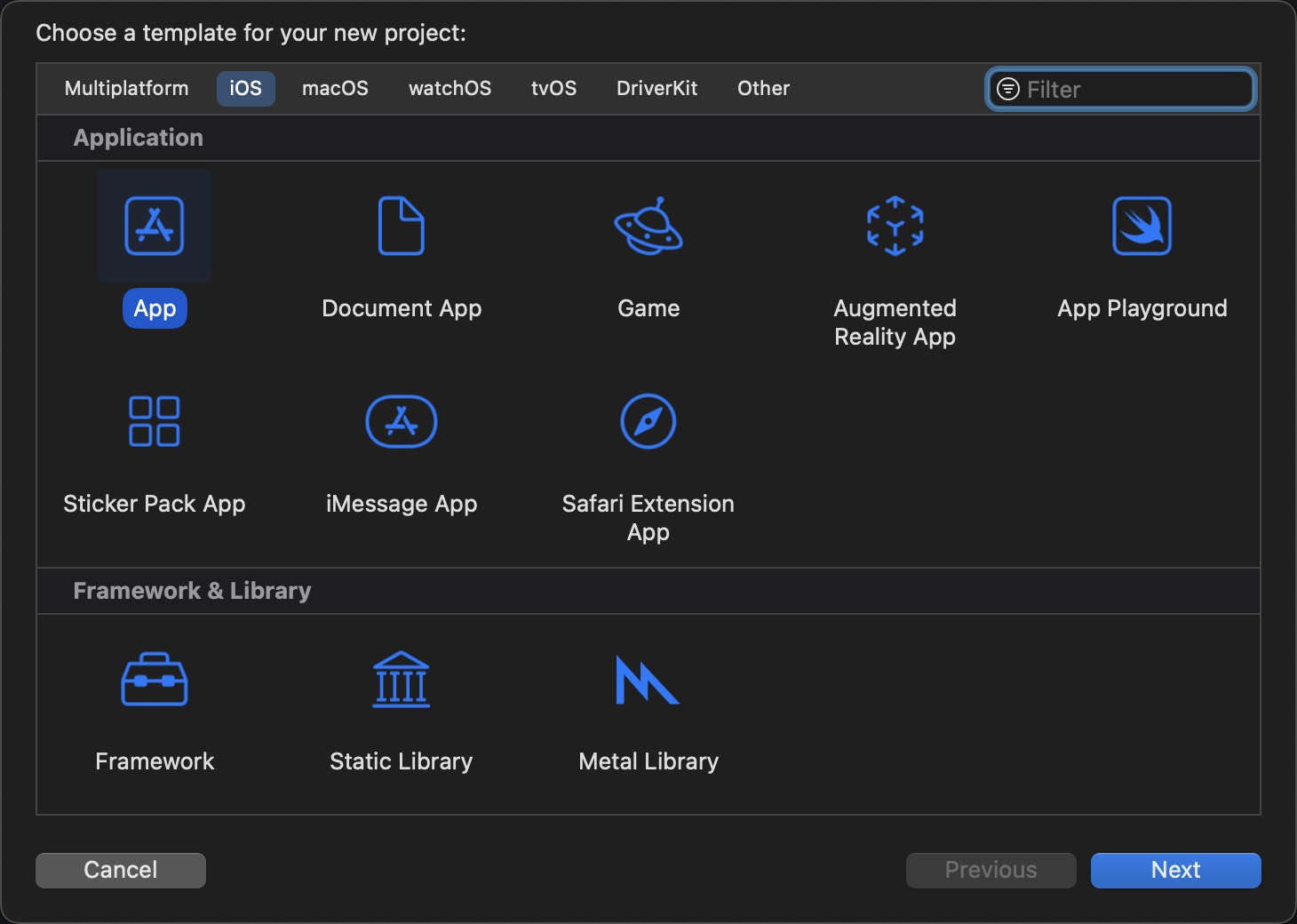
- 运行项目,然后在菜单栏中,选择 Debug > Simulate Location;
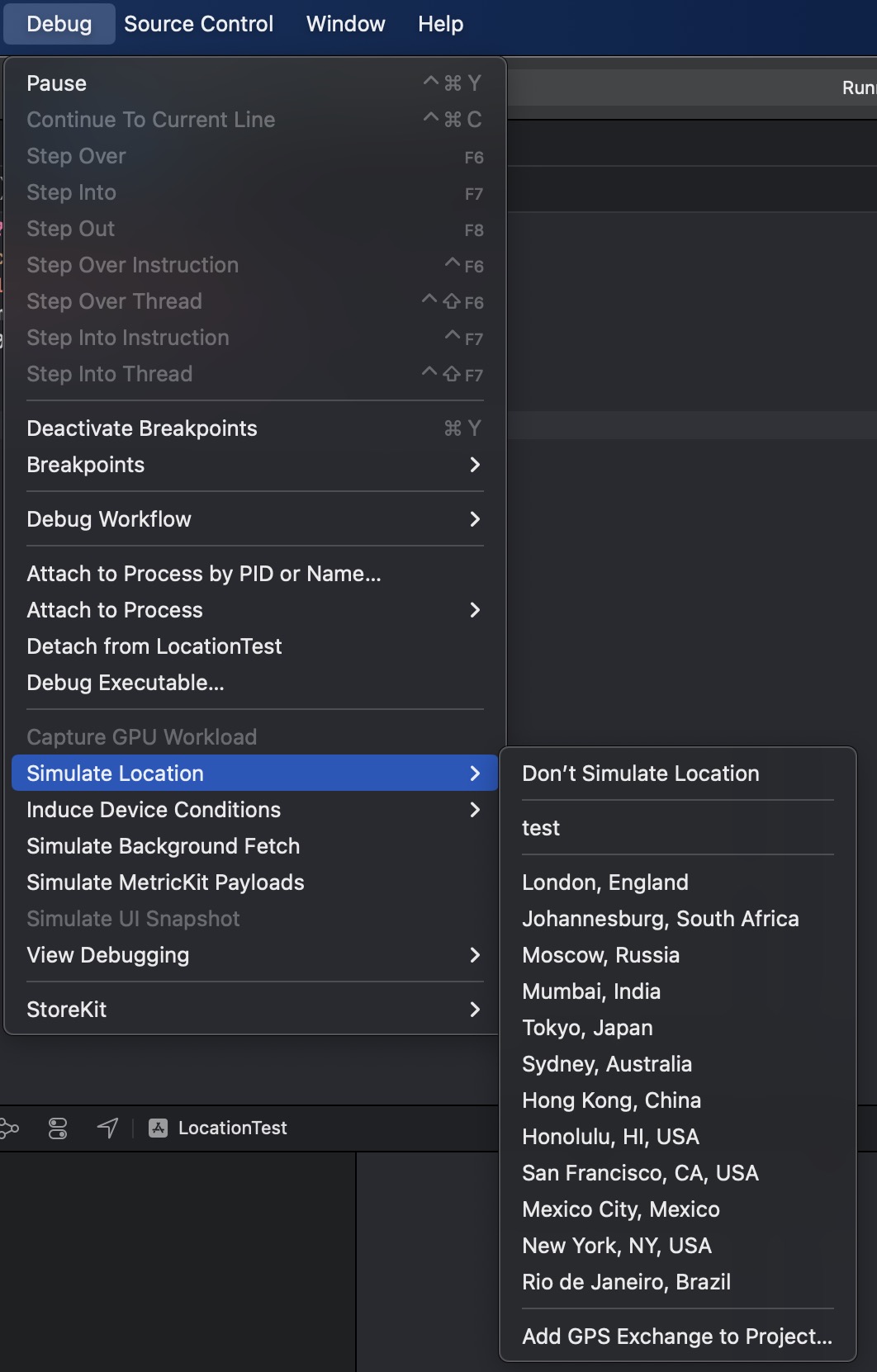
- 在 Simulate Location 窗口中,选择
Xcode预设的一些位置,或者通过GPX文件修改即可;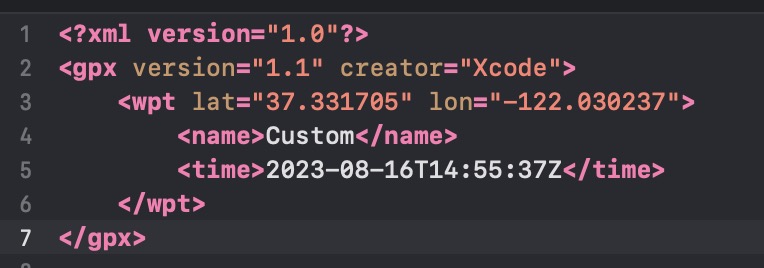
Usbmux
不管是Xcode、iTunes还是第三方的Mac/PC应用,都是通过Usbmux去调用iOS的com.apple.dt.simulatelocation服务。
Usbmux是可以通过一个usb管道建立多个连接的系统,他提供了一个类似TCP的系统,启动主机的进程连接到移动设备的端口号上,在Mac上,是由/System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/MobileDevice.framework/Resources/usbmuxd处理,这是一个由 launchd 启动的守护进程

它在 /var/run/usbmuxd 处创建一个监听 UNIX 域socket。然后usbmuxd通过USB监视设备连接,并和设备进行通讯。
usbmuxd建立了连接之后,iTunes/Xcode会通过MobileDevice.framework调用一些功能,通过class-dump可以发现一些安装DeviceSupport、固件升级、启动服务等的类:
而MobileDevice.framework只存在于Mac,通常会使用开源的libimobiledevice,他不仅实现了usbmuxd监听,并且为没有公开的服务进行的封装,iOS的性能测试、自动化测试基本都离不开它。
识别虚拟定位的方法
isSimulatedBySoftware & isProducedByAccessory
既然有攻,就会有守,先试试看从系统提供的定位API返回的信息中,是否有能有区分出是正常定位,还是虚拟定位。
在查阅了Apple的文档后发现,在iOS 15之后,是有提供CLLocationSourceInformation定位来源可以区分是否是软件产生的虚拟定位或者是外设产生的虚拟定位。
@available(iOS 15.0, *)
open class CLLocationSourceInformation : NSObject, NSCopying, NSSecureCoding {
public init(softwareSimulationState isSoftware: Bool, andExternalAccessoryState isAccessory: Bool)
/*
* isSimulatedBySoftware
*
* Discussion:
* Set to YES if this location was detected as being generated by a software simulator, such as Xcode
*/
open var isSimulatedBySoftware: Bool { get }
/*
* isProducedByAccessory
*
* Discussion:
* Set to YES if this location was generated from an external accessory, such as CarPlay or an MFi accessory
*/
open var isProducedByAccessory: Bool { get }
}
经过测试后,这两个字段确实是有用的,正常定位的时候:
public func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
print("是否是其他软件生成:\(locations.first?.sourceInformation?.isSimulatedBySoftware ?? false)") // 是否是其他软件生成:false
print("是否是其他配件生成:\(locations.first?.sourceInformation?.isProducedByAccessory ?? false)") // 是否是其他配件生成:false
}
使用其他软件修改定位的时候:
public func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
print("是否是其他软件生成:\(locations.first?.sourceInformation?.isSimulatedBySoftware ?? false)") // 是否是其他软件生成:true
print("是否是其他配件生成:\(locations.first?.sourceInformation?.isProducedByAccessory ?? false)") // 是否是其他配件生成:false
}
altitude & verticalAccuracy
而在iOS 15之前,系统的没有提供的,查阅了网上的资料后,发现如果是虚拟定位CLLocation的altitude(海拔)总是会返回0,verticalAccuracy(精度)只会返回-1,所以测试了一下,使用正常定位的时候:
public func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
print("location altitude:\(locations.first?.altitude)") // location altitude:Optional(27.427248001098633)
print("location verticalAccuracy:\(locations.first?.verticalAccuracy)") // location verticalAccuracy:Optional(17.320518493652344)
}
使用其他软件修改定位的时候:
public func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
print("location altitude:\(locations.first?.altitude)") // location altitude:Optional(0.0)
print("location verticalAccuracy:\(locations.first?.verticalAccuracy)") // location verticalAccuracy:Optional(-1.0)
}
type
另外CLLocation还有个私有属性type,可以用来区分是否是虚拟定位,正常定位的时候:
let location = locations.first
print(location?.value(forKey: "type")) // 13
使用其他软件修改定位的时候:
let location = locations.first
print(location?.value(forKey: "type")) // 1
逆向
逆向是最头疼的问题,有攻才有防,在你不知道对方用什么招的时候,只能猜测对方会用什么方法,常规的方法,因为越狱后会存在Cydia,并且不再是沙盒权限,可以通过判断Cydia和越狱后才能获取得到的路径:
func isJailedDevice() -> Bool {
let jailPaths = ["/Applications/Cydia.app",
"/Library/MobileSubstrate/MobileSubstrate.dylib",
"/bin/bash",
"/usr/sbin/sshd",
"/etc/apt"]
for item in jailPaths {
if FileManager.default.fileExists(atPath: item) {
return true
}
}
return false
}
越狱只是前提修改定位的前提,我们需要真正保护自己的App不受修改,防止被hook,iOS hook通常是通过注入dylib,替换方法实现达到效果,dladdr可以帮我们验证这个类的实现是来自哪里,在没有被hook的时候:
+ (void)test
{
Dl_info info;
IMP imp = class_getMethodImplementation(objc_getClass("CLLocation"),
sel_registerName(@selector(coordinate)));
if(dladdr(imp,&info)) {
NSLog(@"dli_fname:%s",info.dli_fname);
}
}
上面输出的是:
2023-08-16 23:35:07.194234+0800 LocationTest[2989:383262] dli_fname:/System/Library/Frameworks/CoreLocation.framework/CoreLocation
而被hook后,输出的是:
2023-08-16 23:35:18.194507+0800 LocationTest[2989:383262] dli_fname:/private/var/containers/Bundle/Application/1DB1541C-6997-4895-8850-B77645F4DB94/LocationTest.app/LocationTest
所以我们可以通过这个函数判断是否被hook。
总结
可以通过以下的几个方法识别出iOS的虚拟定位:
- iOS 15以上,可以通过系统新增的两个属性
isSimulatedBySoftware和isProducedByAccessory判断是否是虚拟定位; - 判断海拔
altitude为0,精度verticalAccuracy为-1; - 通过
CLLocation的私有属性type判断,为1的时候,是虚拟定位; dladdr判断是否被hook
请保持转载后文章内容的完整,以及文章出处。本人保留所有版权相关权利。